06/2016
Linkedin Influencers
Translation: Simone Troula
In a historic referendum, the United Kingdom decided to leave the European Union. Maybe you are wondering what it is that you, anywhere outside the UK, have to do with it. Much more than you imagine.
To begin with, the Stock Exchanges plummeted all over the world, indicating that expectations for corporate results and the economy got worse. But why?
No shortage of reasons. This decision shall strengthen an anti-establishment, nationalistic and populist movement in Europe and the USA, increasing uncertainty about the future. This leads companies to be more cautious in their investment and consequently reduces the generation of jobs and the growth of world economy.
Since the turn of the millenium the average growth rate of developed countries was only half what it used to be in the three previous decades. Worse still, it favored capital holders nearly exclusively, alongside a movement towards negative interest rates – there are already over US$ 9 trillion in bonds paying negative interest rates in developed countries. This generated bubbles of financial assets, but weak economic performance made wages increase less than inflation and come down in real terms. The result is that even in the US, which is the developed country with best economic performance this millenium, average income is less today than 30 years ago, in infantion-adjusted terms. In other words, for the first time in the history of the US an average American is worse off than his parents were at his age. This is generating much resentment and a strong witch-hunt movement blaming immigrants and foreigners, as unfortunately it is common in these cases.
In the last European elections, populists and nationalists made significant progress in practically all countries. The most striking examples were the SYRIZA and the Golden Dawn in Greece, the Swiss People Party in Switzerland, the Five Stars Movement and the Northern League in Italy, the Danish People Party in Denmark, the Podemos and the Citizens in Spain, the Jobbik in Hungary, the Finnish in Finland, the National Front in France and the UKIP in the United Kingdom. The current American presidential campaign is no different, with Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders displaying performances that nobody in their right minds could possibly have imagined a while ago.
The United Kingdom leaving the European Union – or Brexit as most people are calling it – will strengthen anti-immigrant and separatist movements, which not only weakens international trade and therefore reduces global growth, but also opens space for even more severe tensions, potentially including wars. It is worth remembering that the interdependence project of European countries intended by the European Union had two goals: to accelerate economic growth and reduce the risk of armed conflict in a region that hosted two World Wars in the last century. Both goals are now weakened.
To make things worse, the negative economic shock comes at a point in time when the global economy was already teetering and potentially threatened by two large financial bubbles.
In the world economy, Europe and Japan already had a very weak performance, and will now probably be thrown into recession. Among the BRICS, Brazil and Russia are already in recession and China is growing less than it used to until recently. Only India is still going well. Since 2009 the US live through the slowest economic recovery since the post-war, coupled with electoral uncertainty and the possibility of interest rate hikes by the Fed, however remote they might have become. None of this helps. In short, the risk of a new global recession is now real.
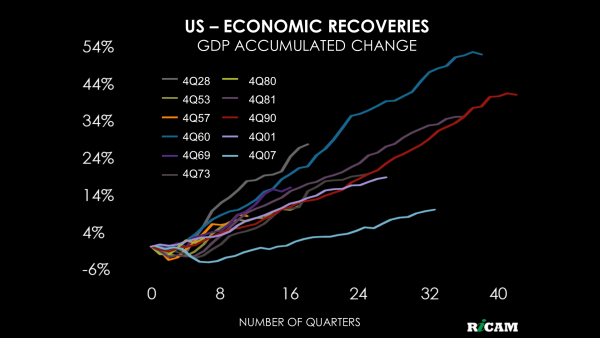
On the financial side, the situation is even more severe. Among the many financial bubbles inflated by tens of trillions of dollars injected in world economy by central banks of developed countries after the global financial crisis of 2008, at least two such bubbles may act as triggers for a new global economic crisis.
The first of them comes from the US. Whereas the economic recovery post-2009 was the weakest since the post-war, the rise in US stock prices was the strongest since then, driven by record profitability of companies. This was possible thanks to several factors that no longer apply:
- In 2008 and 2009 the global financial crisis made unemployment reach the highest level in the US in over 30 years, bringing down wages and increasing the profitability of American businesses. Unemployment has been shrinking since then and it is now less than 5% – which suggests wages will increase, reducing companies’ earnings;
- The exploitation of shale gas doubled power production in the US since 2008, making it cheaper than in the rest of the world, while the price of oil was high in international markets. When oil prices recently dropped from over US$ 100 per barrel to around US$ 50 or less, the American competitive advantage was lost because the American extraction cost is relatively high.
- In 2010 the US dollar was relatively devalued vis-à-vis most other world currencies. This made American exports cheap nearly all over the world, which greatly helped American companies. Between 2010 and 2015 the US dollar began to increasingly regain value – and this should be enhanced by the United Kingdom leaving the European Union. Exports of American products, which were cheap for the rest of the world before, are now expensive – and that reduces sales.
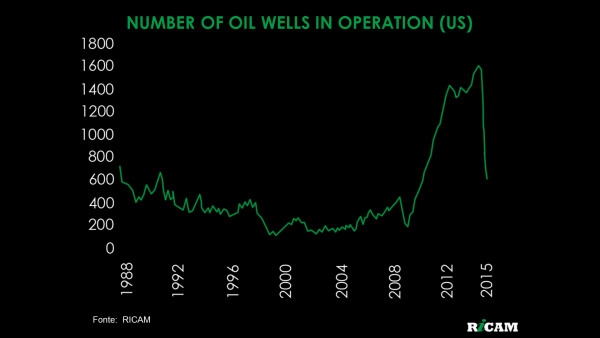
- With extremely low interest rates – even negative recently, American companies managed to cut their financial costs and increase profit. They also issued more debt and used their funds to re-buy stock. Thus, even in the cases when company profits did not grow, profit per share increased because the number of shares – the denominator in the equation – was less. With that, the debt of companies grew considerably, making them vulnerable to possible hikes in interest rates. When the interest rate rises from 5% to 6%, the financial cost of a company increases 20%. When it increases from 0.1% to 1.1%, for the same increase of 1 p.p. the financial cost goes up 1000%.
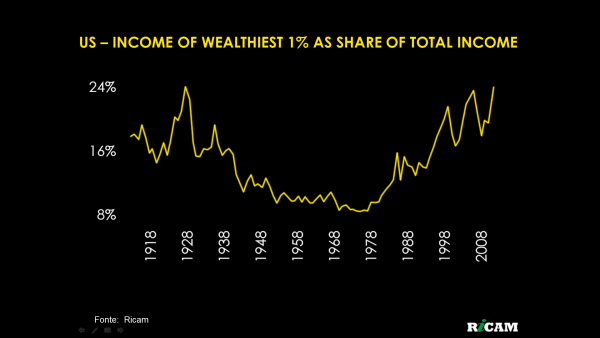
Adding to that, the income concentration in the country is the highest since 1900. Whenever it approached similar levels before – in 1929, in 2000 and in 2008 – there were stock bubbles bursting. This happens because when there is much income concentration and therefore too many people have too low income, the only way they can increase consumption is by getting increasingly indebted. This great indebtedness ends up causing a default crisis when interest rates or unemployment rise.
Finally, it is not just the profit of American companies that is dwindling for nearly two years now and will probably keep going down, but the Price/Profit ratio of American shares is now at the second highest level since 1870, if we consider the mean profit of a whole economic cycle (or Shiller’s CAPE, for financial jargon lovers). Only during the Nasdaq Bubble were American shares ever more expensive according to this indicator. The more expensive stocks are, the greater is the fall, usually, when they start to plummet.
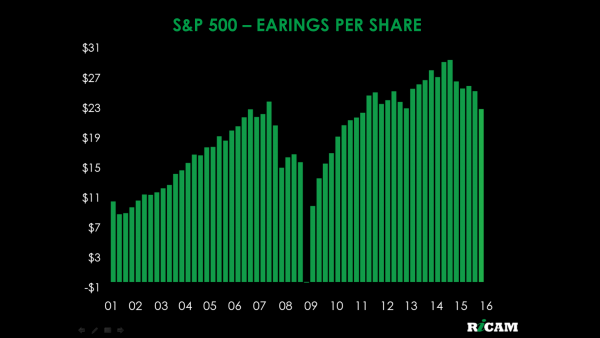
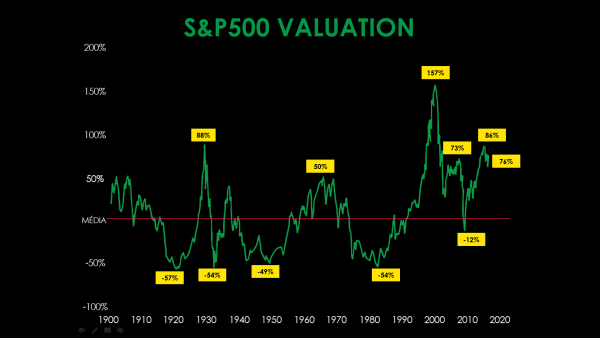
With all these ingredients, a sudden drop of about 50% in the S&P500 (the main stock index in the US) will be no surprise, as happened in 2008/2009. If it happens, though, it will throw the world in a new global financial crisis.
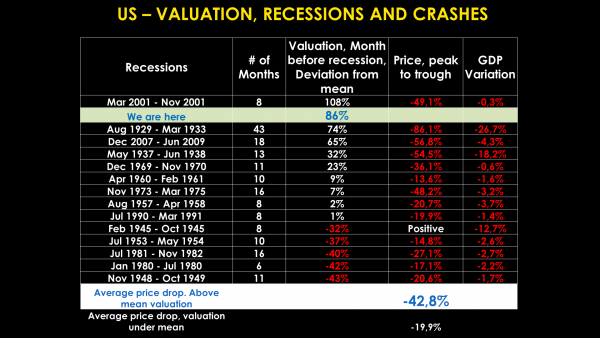
If global economic and American financial problems are not enough, there is still a huge real estate bubble in China that may burst as a result of global recession and/or the bursting of the US stock market bubble.
Beginning with the real estate bubble, it is the largest seen on the planet since at least the mid-1900s – which is the period for which I found data. Just to give an idea, new house and and apartment sales in the US peaked in 2005 at 2.2 million units – and in China the peak was 22 million units last year.
To use another parameter, per capita annual consumption of cement at the height of the American real estate bubble in 2008 was hardly over 400kg. In the most inflated real estate bubble that ever burst – at least by this indicator – the Korean bubble of 1997 was at 1.550kg. In China, it is currently at 1.700kg. Let us remember this is per inhabitant. And there is no shortage of inhabitants in China.
When real estate bubbles burst, home buyers and builders are incapable of honoring their debts with the financial sector, causing great losses to the financial sector and making credit unavailable, which trigger financial bubbles to burst.
When this mechanism push Lehman Brothers into bankrupt in September 2008, starting the global financial crisis, the total assets in the American financial system was US$ 6 trillion. In the Chinese financial system there was little over US$ 3 trillion. Since then, China inflated a credit bubble at a rate never seen before. The total assets in the Chinese financial system are now over US$ 15 trillion – two-point-five times what it was in the US when Lehman Brothers went broke. Most of it was directly or indirectly related to the financing of the real estate bubble. Not to mention the humongous extra-bank financing system – the shadow banking – and the large volume of financing of Chinese real estate companies via the international capital market. In short, it is hard to imagine that when the Chinese real estate bubble bursts we shall not have a new global financial crisis, maybe the most extreme this living generation ever saw.
It is too early to tell whether Brexit will be just the fall of an isolated domino piece – let us hope that it is – or the first in a row of increasingly big dominoes more connected to other dominoes, potentially capable of causing a significant impact on all lives on the planet in the coming years.
For me and my fellows in Brazil this is particularly important because, as I have been pointing out, Brazil has today all the required conditions to isolatedly resume economic growth. And it can do so faster and more strongly than anyone imagines if it recovers the confidence of investors, businessmen and consumers, by tidying public accounts and approving reforms on social security and adopting a cap on government spending. I am so convinced of this that I as much as wrote a book – “Depois da Tempestade” (“After the Storm”) – to explain my reasons in detail.
However, Brazil is not an island. What happens in the rest of the world may sometimes have a significant impact on us. As the Brazilian storm shows the first signs that it may end, clouds appear of what may come to be a major global storm. The similarities with so many other countries and even continents that were fighting hard to end recessions, such as Russia, or to avoid new recessions, such as Europe and Japan is appalling.
Ricardo Amorim is the author of Depois da Tempestade, (After the Storm), one of the hosts of Manhattan Connection, a TV show on Globonews, CEO of Ricam Consultoria, the most influential brazilian on LinkedIn, the only Brazilian on the Speakers Corner list of the best and most important world lecturers and Brazil’s most influential economist according to Forbes Magazine.
Click aqui to get to know Ricardo’s lectures. .
Follow him on : Facebook, Twitter, Instagram e YouTube.




